
DeFi 101: What is Slippage?

Slippage is a must-have concept for any investor involved in cryptocurrency trading. Understanding what slippage is will help you better control investment performance as well as avoid unnecessary risks when the market fluctuates sharply.
What is Slippage?
Slippage is the factor that represents the difference between the expected price of an order and the actual price when a trade is executed. This usually happens when the market is highly volatile, with many people trading at the same time causing the asset’s rate to change continuously.
For example, at the time you place a sell order, 1 BTC = $30,000. After executing the order, you only get $29,700. So the slippage is now 1%, which means BTC has decreased by 1% while you are trading.
What causes Slippage?
In the cryptocurrency market, slippage can affect investor profit/loss results. Some of the main causes of slippage include:
- Market volatility: During downtrend or uptrend period, traders tend to buy and sell continuously, resulting in many assets changing in price in a short time.
- High volume: Some assets suddenly emerge due to news and events (such as LUNA token in the past time) that will be of special interest to many people, then the trading volume will become higher increase dramatically. Asset prices can fluctuate greatly within 1 second.
- Low liquidity: Some assets are not traded frequently, resulting in insufficient liquidity. Users who place orders to buy and sell these assets often suffer from high slippage, which greatly affects investment efficiency.
Positive Slippage and Negative Slippage
Most people think slippage is bad for trading. In fact, slippage is of two types, positive slippage and negative slippage.
For buying orders, slippage is positive when the actual price is lower than the order price, the user can buy it at a better price than expected. Meanwhile, slippage is negative when the bid price is higher than the intended entry price.
For selling orders, slippage is positive when the actual price is higher than expected, users will receive more than expected when selling. Meanwhile, slippage is negative when the actual selling price is lower than intended to sell.
Slippage in DeFi
Slippage is inevitable when participating in any market (stocks, forex, …), but it happens most often and is most obvious in the cryptocurrency market, especially in Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
When trading on any decentralized platform like DEX (PancakeSwap, Uniswap…) or through DeFi wallets (RICE Wallet, Trust, Metamask,…), users need to know how to adjust the slippage accordingly so that the transaction takes place quickly and successfully with as little loss as possible.
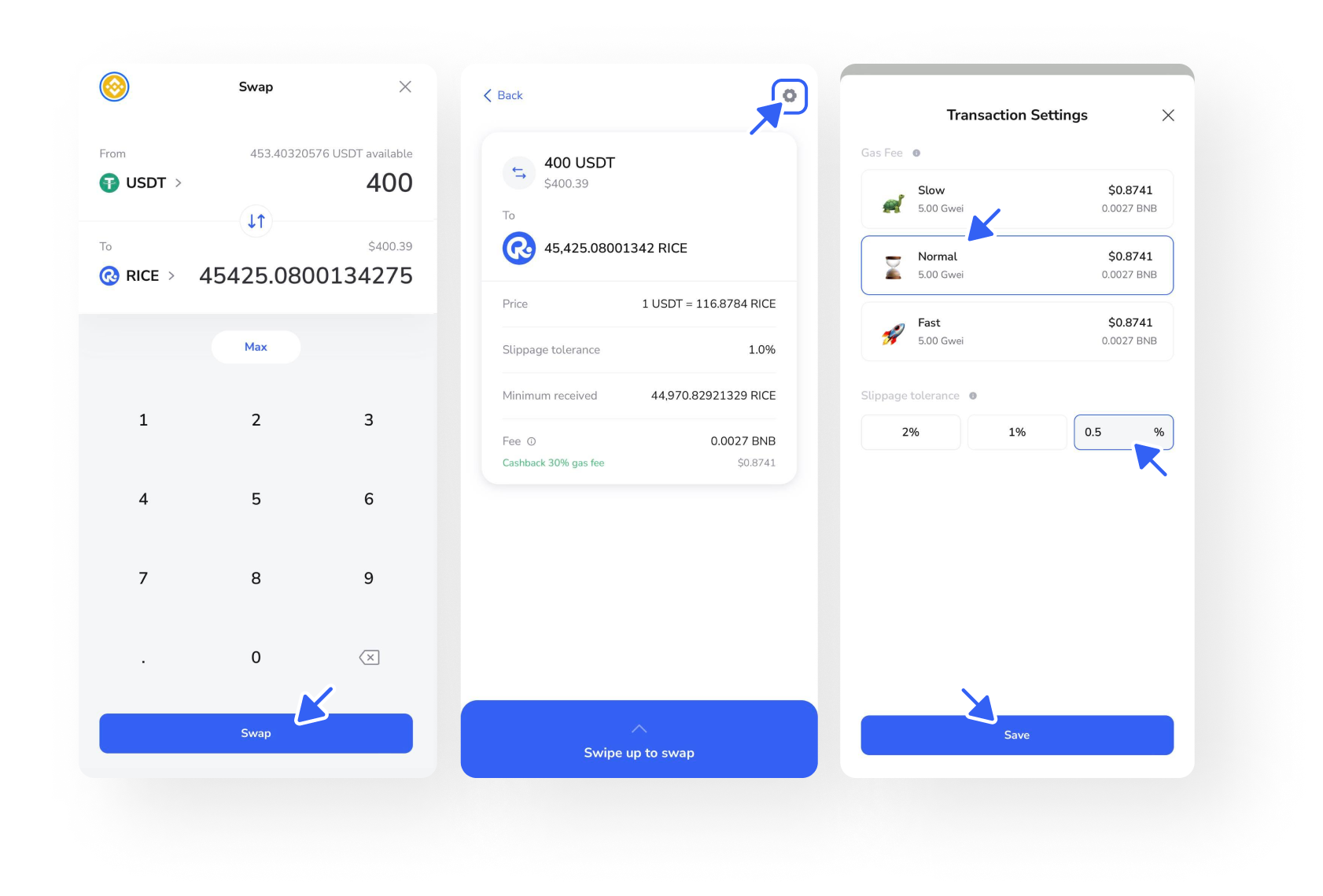
- For assets with good liquidity and stable trading volume, suitable slippage is 0.5 – 1%.
- For assets that are highly volatile, the slippage can be as high as 5 – 10% or more.
- Some assets have default slippage required by the project for a minimum tax rate for successful transactions, typically Auto-Staking tokens such as TITANO, LIBERO,…